
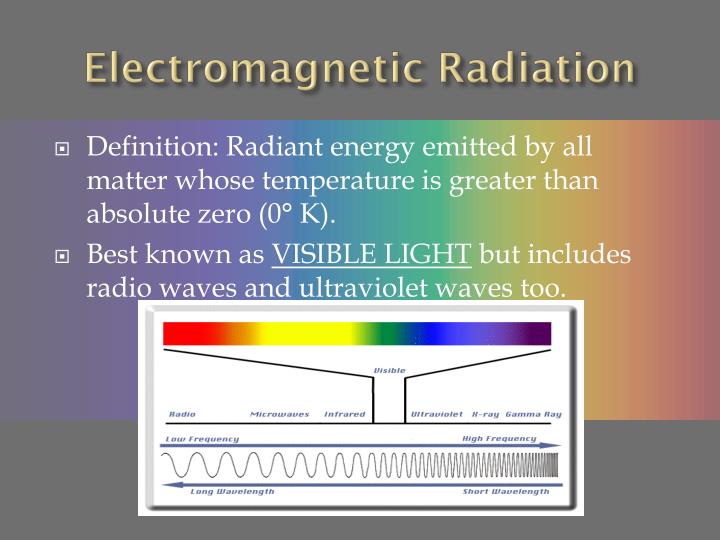
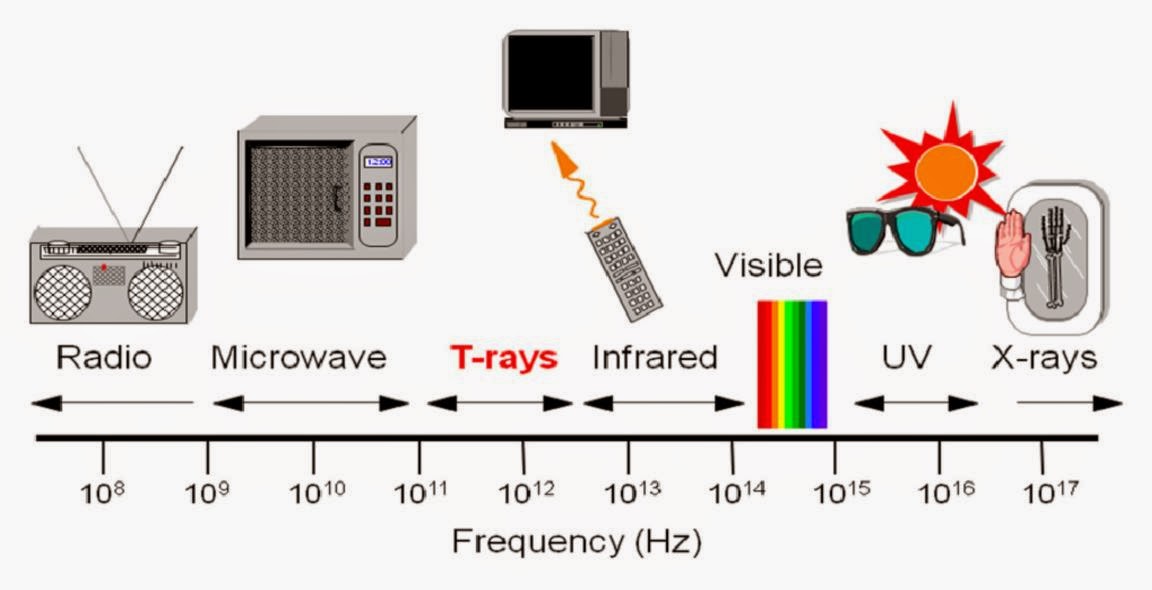
But these relatively large wavelength (and low frequency) electromagnetic waves are also used in radar applications. Unsurprisingly, the radiant energy of microwaves are used to heat up food in microwave ovens. Radio waves have the l ongest wavelengths of any wave in the electromagnetic spectrum, and the lowest frequencies, as well. You’re probably familiar with radio waves, as these are what we use when we adjust the dial in our car to find that perfect tune. Here they are, ordered from lowest frequency to highest: Radio Waves Radiant energy is transferred through the emission of electromagnetic radiation, and there are seven different forms across the electromagnetic spectrum. This means that electromagnetic radiation with higher frequencies transfers more radiant energy. Waves with higher frequencies carry with them more energy. Conversely a wave with a short wavelength will repeat more often, and therefore have a higher frequency. The frequency of a wave is inversely proportional to its wavelength - the longer the wavelength, the less often it repeats in a given period, and therefore the lower its frequency. This is taken by measuring the distance from one peak of the wave to the next peak of the wave.įrequency describes how often the wave repeats its pattern in a given period. Wavelength describes how long the repeated portion of a wave is. To better understand how radiant energy works, we should define three terms used to describe these waves:Īmplitude describes the height of a wave, taken by measuring from the peak all the way down to the trough of the wave. In the case of electromagnetic radiation, the energy being transferred through photons that travel these waves is radiant energy.

These waves work the same as the ones we might see at the beach: They have peaks and valleys, they move more or less in a regular pattern, and they transfer energy as they move. This unit measures the energy of electromagnetic radiation emissions, which is also known as radiant energy. Radiant energy is measured in joules, sometimes abbreviated as J.

When we observe gravitational waves moving through space, the energy they carry is radiant energy. Radiant energy is also used to describe the energy transferred by gravitational radiation. That energy, transferred by electromagnetic radiation through waves, is called radiant energy. Of the fundamental forces of the universe, electromagnetism describes energy that’s transferred by waves through space at the speed of light. Most of the time when the term radiant energy is used, it’s to describe energy transferred by electromagnetic radiation, most often by particles called photons. If that sounds complicated, it’s easier to understand if we take it piece by piece. Radiant energy is the energy transferred by electromagnetic or gravitational radiation. What Is the Definition of Radiant Energy? Here’s your complete guide to radiant energy. If you’ve never heard of radiant energy in this context, don’t worry - we’ve got you covered. But radiant energy is more than just a way to describe someone’s glow it’s an important part of physics, and a way in which we understand our universe. If you’ve had a particularly good hair day, you might’ve heard someone describe you as looking radiant.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
